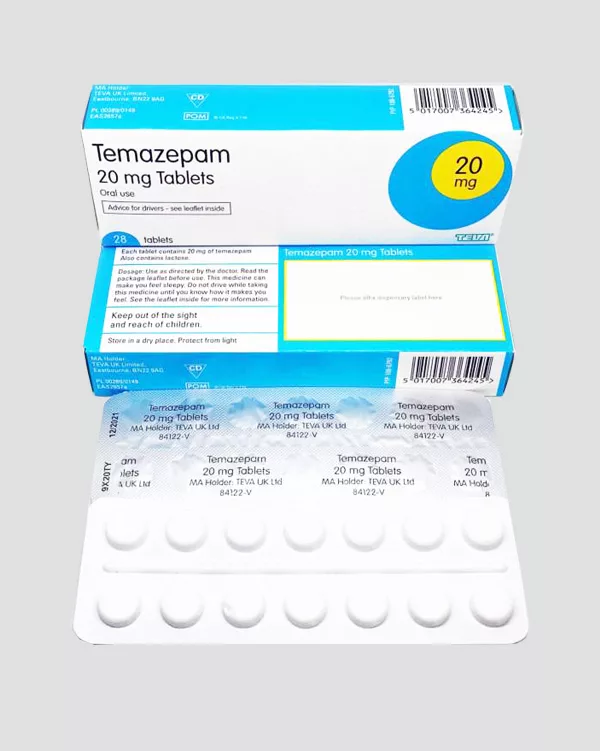
Temazepam 20mg USA
$45.00
Temazepam 20mg is a prescription benzodiazepine medication, most commonly recognized under the brand name Restoril. It is a potent, intermediate-acting sedative-hypnotic prescribed primarily for the short-term treatment of severe insomnia that significantly impairs daily functioning.
It works by enhancing the effect of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), the brain’s main calming neurotransmitter, to produce a strong sedative effect. This action helps to induce sleep quickly, reduce nighttime awakenings, and increase total sleep time.
Temazepam 20mg USA: An In-Depth Guide to a Potent Hypnotic Agent
Introduction
Temazepam, commonly encountered under the brand name Restoril, is a benzodiazepine derivative with potent hypnotic properties, and the 20mg dosage represents a standard therapeutic strength for the treatment of insomnia. Classified as a Schedule IV controlled substance in the United States and similarly regulated worldwide, temazepam occupies a specific niche in sleep medicine due to its distinctive pharmacokinetic profile. Unlike many of its longer-acting counterparts, temazepam is considered an intermediate-acting benzodiazepine, a characteristic that has shaped both its clinical applications and its risk profile. This comprehensive 2000-word exploration will dissect the pharmacology, therapeutic uses, significant risks, and societal context of temazepam 20mg, providing a crucial resource for understanding this powerful, yet double-edged, sedative-hypnotic.
Temazepam 20mg USA
Chemical and Pharmacological Profile
Class and Mechanism of Action
Temazepam is a 1,4-benzodiazepine, a class of psychoactive drugs whose primary mechanism lies in modulating the central nervous system’s (CNS) primary inhibitory network. Its action is not unique in kind but is notable for its selectivity and timing.
Temazepam 20mg USA
GABAergic Enhancement: The brain’s most abundant inhibitory neurotransmitter is gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). When GABA binds to the GABA-A receptor—a chloride ion channel complex—it opens the channel, allowing negatively charged chloride ions to flood into the neuron. This influx hyperpolarizes the cell membrane, making the neuron less likely to fire an action potential, resulting in a net calming or depressant effect on neural activity.
Temazepam 20mg USA
Temazepam, like all classical benzodiazepines, acts as a positive allosteric modulator at a specific binding site on the GABA-A receptor. It does not directly open the channel like GABA itself. Instead, its binding dramatically increases the affinity of the GABA-A receptor for GABA. When temazepam is present, the inhibitory signal produced by any endogenous GABA release is significantly amplified. This widespread enhancement of GABAergic tone in key brain regions, particularly the limbic system (emotional regulation), the thalamus (sensory gatekeeper), and the reticular activating system (arousal and consciousness), produces the drug’s signature effects: profound sedation, anxiolysis, muscle relaxation, and anticonvulsant activity.
Temazepam 20mg USA
Pharmacokinetics: The “Intermediate-Acting” Distinction
The pharmacokinetic profile of temazepam 20mg is its defining clinical feature, setting it apart from other benzodiazepines.
-
Absorption and Onset: Temazepam is well absorbed after oral administration. However, its onset of action is not immediate. Peak plasma concentrations are typically reached in approximately 1 to 2 hours post-ingestion. This makes it less suitable for patients whose sole complaint is sleep initiation (long sleep latency) and more appropriate for those who need help staying asleep. Patients are generally instructed to take it 30-60 minutes before bedtime.
Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Metabolism (A Key Differentiator): Temazepam undergoes minimal hepatic metabolism. It is primarily conjugated directly to an inactive glucuronide metabolite. This is a critical point:
-
It is not metabolized by the cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme system. This reduces its potential for pharmacokinetic drug interactions with the vast array of medications that inhibit or induce CYP450 enzymes (e.g., certain antibiotics, antifungals, antidepressants).
Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Its metabolism is less affected by liver disease compared to benzodiazepines that require oxidative metabolism (like diazepam or alprazolam), though caution is still advised.
-
-
Elimination and Half-Life: Temazepam has an intermediate elimination half-life, ranging from 8 to 20 hours (average ~10 hours). This is shorter than long-acting agents like diazepam or flurazepam but longer than ultra-short-acting drugs like triazolam.
-
Clinical Implications of its Half-Life:
-
Therapeutic: It is effective at preventing middle-of-the-night and early morning awakenings, providing coverage throughout the sleep period.
Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Adverse Effects: The intermediate half-life reduces, but does not eliminate, the risk of “next-day sedation” or residual “hangover” effects (drowsiness, impaired coordination, cognitive blunting). These effects are common, especially during the first few days of therapy or if sleep is truncated.
-
Dependence & Withdrawal: Its half-life influences the onset of withdrawal symptoms. Abrupt discontinuation after regular use can lead to a withdrawal syndrome that may begin within 24-48 hours, which is sooner than with long-acting agents.
Temazepam 20mg USA
-
-
Clinical Applications and Therapeutic Uses
The primary and sole FDA-approved indication for temazepam is the short-term treatment of insomnia. The emphasis on “short-term” cannot be overstated; prescribing guidelines consistently recommend durations not exceeding 7 to 10 days, and only after non-pharmacological interventions have been considered or attempted.
1. Treatment of Severe, Transient Insomnia
Temazepam 20mg is reserved for cases of severe, disabling insomnia that causes marked distress or impairment in social, occupational, or other important areas of functioning. It is particularly considered for:Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Sleep Maintenance Insomnia: Its duration of action makes it a candidate for individuals who frequently wake up and cannot return to sleep.Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Situational Insomnia: Caused by acute stress, hospitalization, or significant life disruptions, where a brief course of medication may be justified alongside coping strategies.
Temazepam 20mg USA
It is crucial to understand that while temazepam increases total sleep time, it, like most hypnotics, disrupts normal sleep architecture. It typically suppresses deep, restorative slow-wave sleep (Stage N3) and can reduce rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, the stage associated with dreaming and memory consolidation.Temazepam 20mg USA
2. Premedication for Anxiety and Insomnia Prior to Medical Procedures
Outside its labeled use, temazepam is sometimes employed off-label as a premedication before surgery or uncomfortable medical/dental procedures. Its combined anxiolytic and sedative effects can help reduce preoperative anxiety and promote amnesia for the perioperative period.
3. Adjunct in Specialized Detoxification Protocols
In some medically supervised alcohol or benzodiazepine withdrawal protocols, temazepam’s intermediate half-life can be utilized in a tapered regimen to mitigate withdrawal symptoms and prevent seizures, though longer-acting agents like diazepam are often preferred for smoother tapering.
Dosage and Administration
The recommended adult dose for insomnia is 15mg to 30mg taken orally once daily, immediately before bedtime. The 20mg strength sits in the middle of this range, often serving as a standard dose after initial tolerance is assessed.
Critical Administration Guidelines:
Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Timing: Must be taken only when the patient can dedicate a full 7-8 hours to uninterrupted sleep. Taking it too late or with less time for sleep dramatically increases the risk of dangerous residual sedation upon waking.
-
Duration: Treatment should be as short as possible. Prescribers are advised to evaluate the need for continued therapy after just a few days. It is not intended for long-term management of chronic insomnia.Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Elderly or Debilitated Patients: A lower initial dose of 7.5mg to 15mg is strongly recommended due to increased sensitivity to benzodiazepines, leading to a higher incidence of ataxia (imbalance), confusion, falls, and excessive sedation.
-
Contraindication with Opioids: Concomitant use with opioid medications is contraindicated due to the black box warning for profound respiratory depression, coma, and death.Temazepam 20mg USA
Side Effects and Adverse Reactions
The adverse effects of temazepam 20mg are direct extensions of its CNS-depressant pharmacology.
Common Side Effects:
-
Central Nervous System: Drowsiness, dizziness, lethargy, “hangover” feeling, headache, ataxia (loss of coordination), and anterograde amnesia (difficulty forming new memories after taking the drug).
-
Psychiatric: “Paradoxical reactions” occur in a subset of patients, particularly the elderly and children. These include excitatory states such as increased anxiety, agitation, aggression, irritability, hallucinations, and vivid nightmares.
-
Gastrointestinal: Dry mouth, nausea, diarrhea.
-
Neuromuscular: Muscle weakness.
Serious and Dangerous Adverse Effects:
-
Complex Sleep Behaviors: Perhaps the most alarming rare side effect associated with hypnotics like temazepam is the risk of engaging in activities while not fully awake, with no subsequent memory of the event. This includes sleep-driving, sleep-walking, preparing and eating food, making phone calls, or engaging in sexual behavior. These behaviors can result in serious injury or death to the patient or others.Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Respiratory Depression: Temazepam can suppress the brainstem’s drive to breathe. This risk becomes catastrophic when combined with other CNS depressants like alcohol, opioids, barbiturates, or other sedatives. The combination with opioids carries a FDA-mandated Boxed Warning.
-
Profound Dependence and Addiction: Physiological dependence can develop within weeks of regular use, even at therapeutic doses. Psychological addiction, characterized by compulsive drug-seeking behavior, is a significant risk, particularly in individuals with a history of substance use disorder.
-
Severe Withdrawal Syndrome: Abrupt discontinuation after chronic use precipitates a withdrawal syndrome that mirrors rebound CNS hyperexcitability. Symptoms range from rebound insomnia and anxiety to tremors, sweating, nausea, perceptual disturbances, and, in severe cases, grand mal seizures and delirium tremens, which can be fatal.
-
Increased Fall and Fracture Risk: A major public health concern, especially for the elderly. The sedative and ataxic effects significantly increase the risk of falls, leading to hip fractures and associated morbidity/mortality.
-
Tolerance: The hypnotic effect of temazepam diminishes with continued use, often within days to weeks. This can lead patients to independently increase their dose, escalating the cycle of dependence and risk.
Contraindications and Major Drug Interactions
Absolute Contraindications:
-
Hypersensitivity to temazepam or other benzodiazepines.
-
Concurrent use with opioids (except in exceptional, life-saving circumstances under strict medical monitoring).
-
Myasthenia gravis (can worsen muscle weakness).
-
Severe respiratory insufficiency (e.g., severe COPD, untreated sleep apnea).
-
Pregnancy (risk of neonatal flaccidity and withdrawal syndrome) and breastfeeding.
-
Acute narrow-angle glaucoma (though this is more a concern with earlier benzodiazepines).
Major Drug Interactions:
The CNS-depressant effects are additive and potentially synergistic.
-
Alcohol: The combination drastically impairs motor skills and judgment and can lead to dangerous levels of sedation and respiratory depression.
-
Opioids: As stated, this combination is contraindicated and life-threatening.
-
Other CNS Depressants: Including other benzodiazepines, barbiturates, sedating antihistamines, muscle relaxants, and certain antidepressants (e.g., trazodone, mirtazapine) and antipsychotics.Temazepam 20mg USA
-
Drugs Affecting Glucuronidation: While not a CYP450 substrate, drugs that inhibit the UGT enzyme system (responsible for glucuronidation) could theoretically increase temazepam levels, though such interactions are less common and predictable.
The Crisis of Dependence, Tolerance, and Withdrawal
The therapeutic use of temazepam 20mg is fundamentally constrained by its high potential for creating iatrogenic (physician-caused) dependence.
Tolerance: Neuroadaptation occurs rapidly. The brain responds to continuous GABA enhancement by downregulating GABA-A receptors and adjusting other neurotransmitter systems. The 20mg dose that initially produced reliable sedation may become ineffective, tempting dose escalation.
Physiological Dependence: A state where the CNS has adapted to the constant presence of the drug. The normal functioning of the brain’s excitatory/inhibitory balance now requires temazepam. Its absence triggers a hyperexcitable withdrawal state.
Withdrawal Syndrome: Symptoms are the mirror image of the drug’s effects and can be severe.
-
Early (1-2 days): Rebound insomnia (often worse than the original complaint), anxiety, agitation, sweating.
-
Peak (2-5 days): Tremors, nausea/vomiting, tachycardia, hypertension, hyperthermia, perceptual distortions, depersonalization.
-
Severe: Hallucinations, seizures, delirium.
Management of Dependence: Discontinuation after regular use must be medically supervised. An abrupt stop is dangerous. A slow, individualized taper is essential, often reducing the dose by 10-25% every 1-2 weeks. Patient education and support are critical during this challenging process. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) should be implemented to address the underlying sleep disorder without medication.
Societal Impact and Regulatory Context
Temazepam emerged in the 1970s and 80s, an era of high benzodiazepine prescribing. It gained notoriety not only as a prescription hypnotic but also as a drug of abuse, sometimes referred to by street names like “jellies” or “eggs” (referring to the capsule form). Its potential for misuse led to its strict control as a Schedule IV substance under the Controlled Substances Act, indicating a recognized potential for abuse and dependence, albeit less than Schedules I-III.
Temazepam 20mg USA
Prescribing trends have shifted profoundly. The “Z-drugs” (zolpidem, zaleplon, eszopiclone) were initially marketed in the 1990s as safer, non-benzodiazepine alternatives, though they share many of the same risks (dependence, complex sleep behaviors). Today, the gold standard for chronic insomnia is unequivocally Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I), a structured program that addresses the thoughts and behaviors perpetuating sleep problems without medication risks. Hypnotics like temazepam are now viewed strictly as a short-term crisis management tool, if used at all.
Temazepam 20mg USA
Conclusion
Temazepam 20mg is a potent intermediate-acting benzodiazepine hypnotic with a clearly defined but extremely narrow window of appropriate use. Its pharmacokinetic profile offers a specific solution for sleep maintenance insomnia with a somewhat lower risk of next-day effects compared to long-acting agents,Temazepam 20mg USA yet it carries the full burden of benzodiazepine risks: rapid tolerance, high dependence potential, dangerous interactions (especially with opioids), the terrifying possibility of complex sleep behaviors, and a severe withdrawal syndrome.Temazepam 20mg USA
Temazepam 20mg USA
In contemporary medicine, its role has been rightly marginalized. It stands as a reminder of an era when chemical solutions for sleep were pursued aggressively, often overlooking the profound neuroadaptation they induce. For the select patients who may benefit from its short-term use, it demands the highest level of clinical vigilance, clear patient education on risks, and an unwavering commitment to the principle of the shortest possible duration. Ultimately, temazepam 20mg is not a treatment for insomnia but a temporary, high-risk suspension of it, to be deployed with extreme caution and always with an exit strategy firmly in place.Temazepam 20mg USA
| quantity | 28 pills |
|---|
Be the first to review “Temazepam 20mg USA” Cancel reply
Related products
sex pills


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.